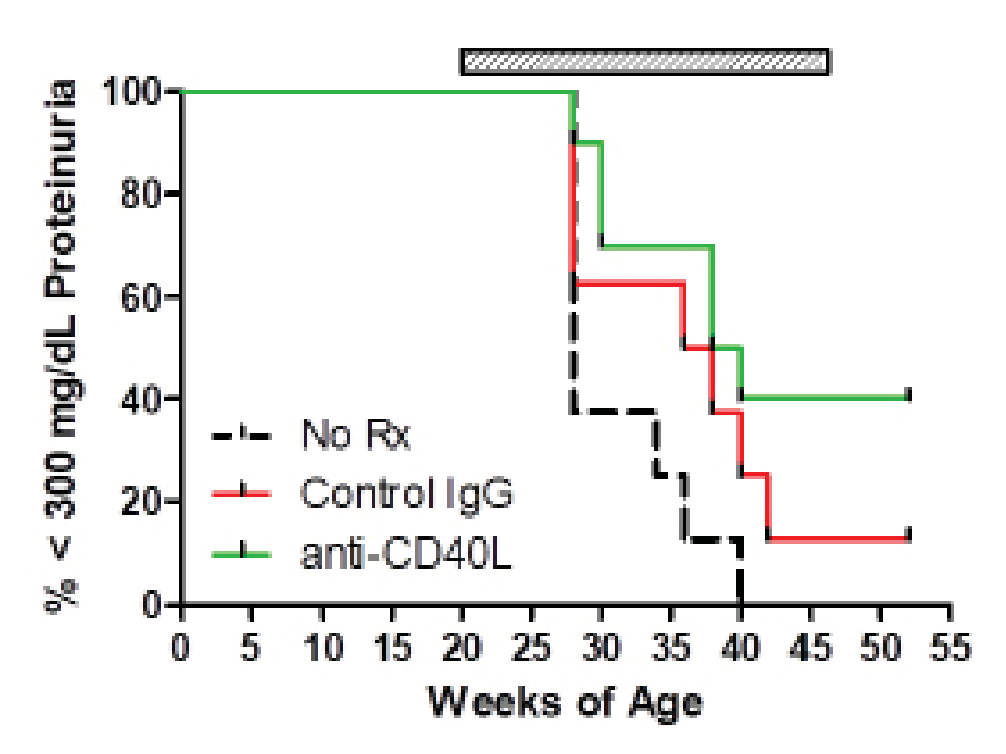
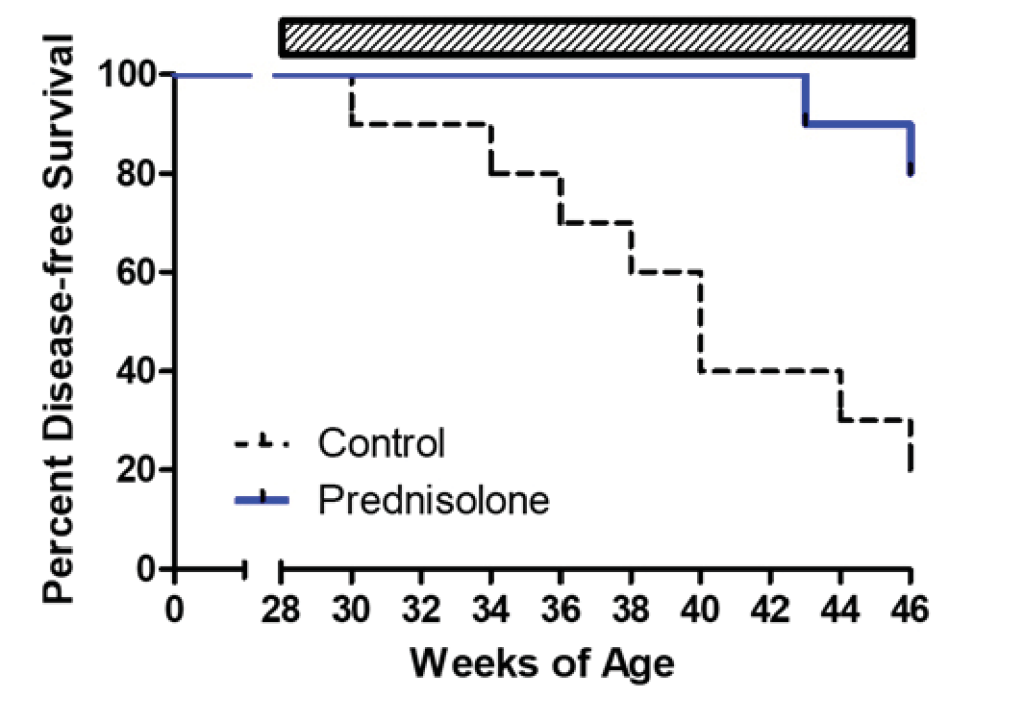
The immune system has been identified as a target organ for adverse effects caused by test material administration. Because of this, the T-Cell-Dependent Antibody Response (TDAR) assay is used to assess potential immunotoxicity and to determine the impact of a test material on the immune response at the preclinical stage of drug discovery. This assay is the gold-standard for studying these effects due to the requirement of multiple immune functions and cell types to generate an antibody response including antigen uptake and presentation, CD4 T cell help, B cell activation and antibody production.
Biomere has validated multiple TDAR models including non-human primates and rodent models.
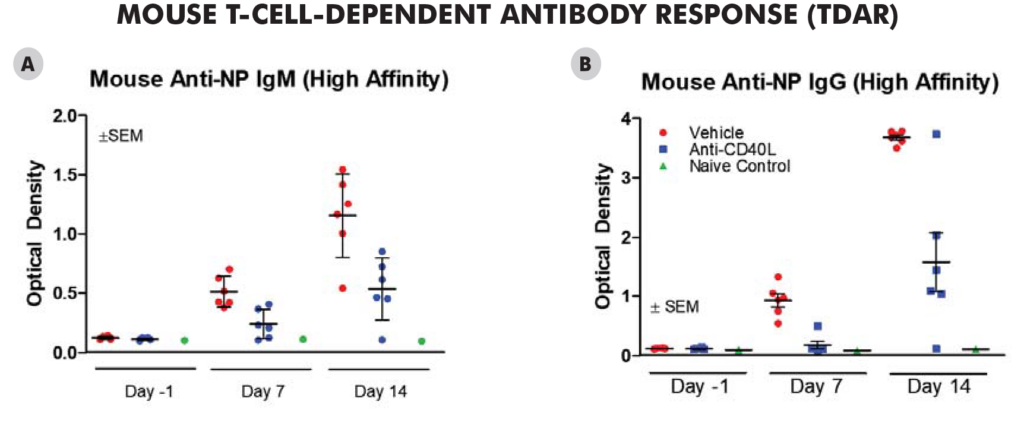

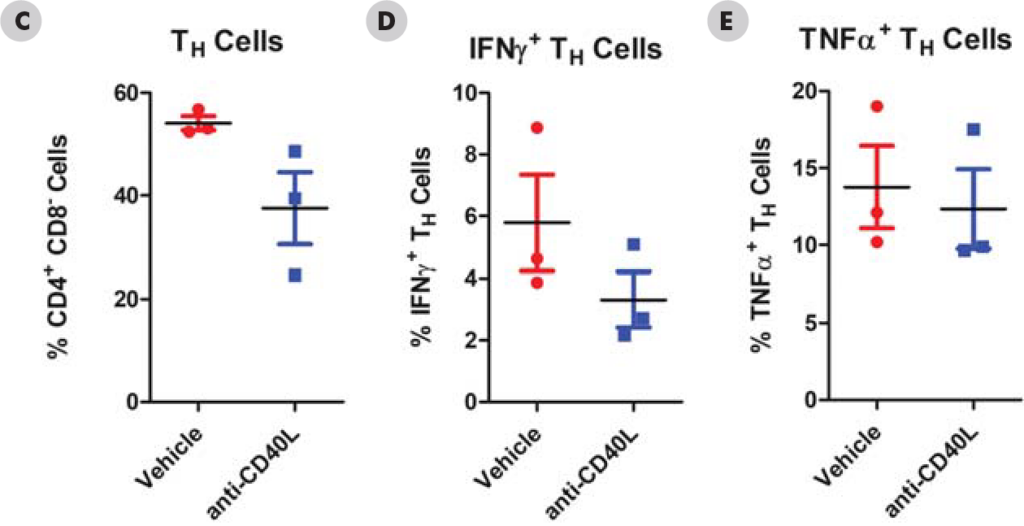
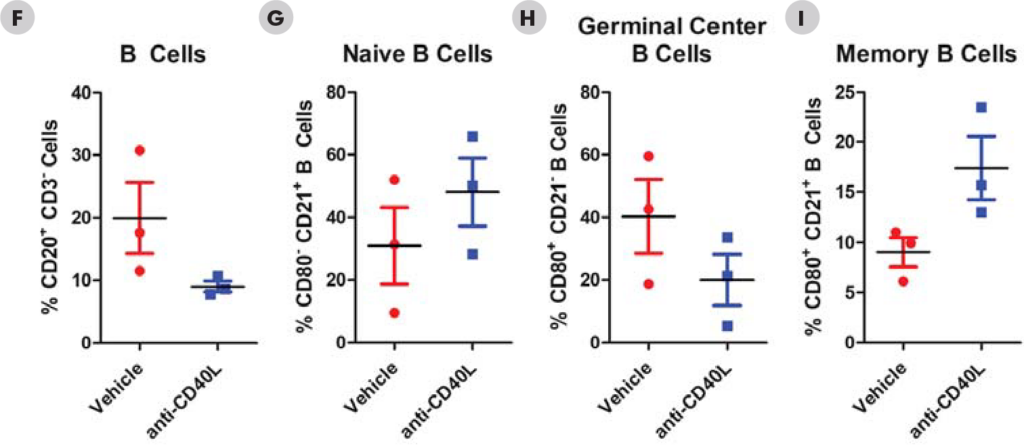
Significant decreases were observed in IgM and IgG antibodies generated in both the mouse and NHPTDAR assays in immune suppressive treatment (α-CD40L) compared to vehicle control. A proportional decrease in germinal center B cells compared to other B cell groups, as well as a decrease in B cells as a total population in α-CD40L versus control were observed. Decreases in the proportion of CD4+ TH cells were also observed in α-CD40L treated versus control, with a decrease in the proportion of IFNγ+ TH cells. From these results, we can see α-CD40L was able to suppress the generation of antibodies against the target antigen and impacted the TH cell and germinal center B cell response.